Cheat Sheet: Application Governance
Accelerating the expansion of IGA Infrastructure
The What
Application governance (and administration) (AGA), is a specialized - yet rising - domain within Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) focused on managing the full lifecycle of access, permissions, and compliance for applications. These apps are typically those involving high-risk factors like privileged access, non-human identities, or shadow IT.
The key end goal design principles include:
Zero Standing Privilege (ZSP): A strategic migration where no identity or account has pre-provisioned permissions or credentials when not in use, thereby reducing the identity attack surface.
Just-in-Time (JiT) Access: Permissions and credentials are associated only when a verified, validated, and approved event or task is being processed.
Automation: Essential for integrating more identities, systems, and locations, which includes automating discovery, provisioning, de-provisioning, and credential rotation.
The Why
Two sub-problems have emerged with respect to successfully deploying concepts like ZSP, JiT and least-privilege as part of a broader identity security fabric and zero trust initiative.
Firstly the existing identity and access management (IAM) pillars being used to handle the B2E workforce life cycle management use cases are often silo’d. This results in visibility blind spots, overlapping capabilities and ineffective security controls assurance.
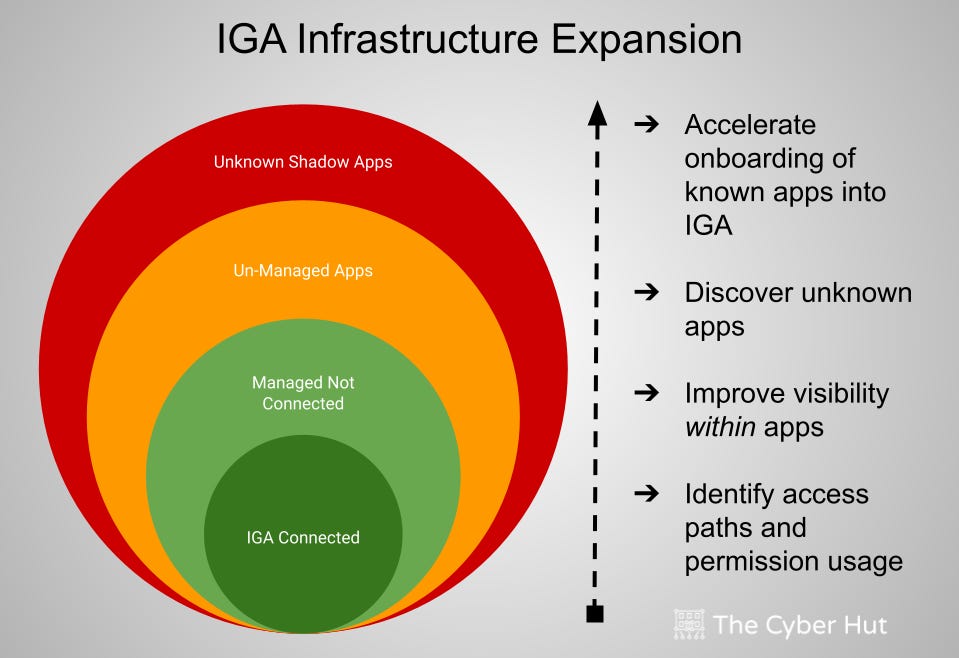
The second aspect, is that specifically within the IGA world, the coverage of the core IGA platforms is low. They typically focus upon the most high risk applications - or applications that fall under regulatory scrutiny. This could be less than 10% of the overall application landscape. The remaining applications are either managed manually using ticketing systems or are entirely un-managed. The un-managed list will also include shadow-apps - that organisations don’t even know are un-managed.
To that end several issues develop:
Organisations want to improve basic IGA coverage to more (if not all apps)
Un-managed and shadow-app risk management is not complete
Visibility and usage within applications is not known
Access request and review processes are incomplete, ineffective and costly
Considerations
Is the existing IGA components (software or manual) being measured?
Is the current IGA model working effectively?
What is hindering expansion of the core IGA capabilities to more systems?
Do you have IGA capabilities for all identity types including NHI, agentic and workloads?
Example Capabilities
Discovery of shadow applications
Analysis of un-managed applications
Accelerated on-boarding of applications into the core IGA function
Visibility of account usage within applications
Support for human and non-human accounts
Composite risk analysis of application configuration
Composite risk analysis of application account usage
Template and semi-autonomous connectivity
Access path analytics
Permission usage analytics
Access request contextual analysis - E.g SoD, compliance validation
Vendor Solutions
Nexis
Offering a solution for “Enterprise Authorization Governance”.
Core Capabilities:
Authorization Governance: Helps organizations manage and structure authorizations, ensuring they undergo lifecycle processes and comply with regulations (like SoD, least privilege).
Overlay for Existing IGA: It acts as an overlay to enhance existing IGA systems (e.g., SailPoint, One Identity, IBM, Oracle, MS Entra ID) for improved functionality and efficiency.
Role Management: It features role mining, fine-grained analysis, risk-based RBAC, and streamlined role lifecycle management (creating, changing, deleting Business Roles).
Workflow Automation: It uses an easy-to-use, no-code workflow engine for seamless implementation of IGA use cases and automating Joiner-Mover-Leaver (JML) processes.
Authorization Concept Management: Its module provides an integrated, automated solution for creating, maintaining, and versioning audit-proof authorization concepts, overcoming the limitations of static documents (like Word/Excel).
AI Integration: Includes an Intelligent Assistant (NICO) to guide users through recertification, and AI-driven features for role model discovery, optimization, and anomaly detection.
User Experience: It’s designed for end-users, providing tailor-made, web-based interfaces and self-service portals.
Solution Scenarios:
Compliance: Simplifying challenges around regulatory compliance, Segregation of Duties (SoD), and recertifications.
Modernize Legacy IGA: Enhancing functionality and efficiency of deeply integrated legacy IGA systems, particularly around user experience and self-service.
IGA Light: Offering smart Identity Governance for Small to Midsize Businesses (SMBs) without existing IGA solutions.
Authorization Governance for Microsoft Entra ID: Enhancing compliance and governance for organizations using Microsoft Entra ID.
Orchid Security
Core Capabilities:
Application Discovery and Inventory Management: Their initial customer landing point is application inventory, focused on finding and identifying un-managed, self-hosted, or previously unknown applications.
Application Governance: Helping organizations govern their applications, especially after they are discovered.
Identity and Access Analysis: They provide insights into:
Authentication flows and access paths.
Routes, authentication methods, and access happening within the applications.
The difference between Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) and activity via traceability.
Risk Analysis and Compliance:
Applications are presented via a risk analysis dashboard.
They provide out-of-the-box templates, scans, and recommendations for compliance frameworks such as ISO 27001, NIST 800-53, PCI DSS, SOC 2 Type 2, GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX.
Augmentation and Remediation: They can “augment and raise the security level” if an issue is found, particularly for legacy applications that cannot be changed, supporting inline remediation.
Solution Scenarios:
Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A): Providing due diligence, risk analysis, and counter measures during app integration.
Audit Failings and GRC Concerns: Addressing audit findings and Governance, Risk, and Compliance issues.
IGA Expansion and Onboarding Acceleration: Speeding up the integration of disconnected applications.
Understanding Out-of-Band Authentication Flows.
Readibots
Core Capabilities:
Readibots provides a platform focused on Identity Data Automation to streamline and accelerate Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) processes. They position their product as an IAM Hub built to remove manual effort and complexity from identity flows.
Focus on Automation: Core offering is the READI platform, which focuses on automating identity data flows. This is presented as an alternative to traditional connectivity or workflow engines, aiming to solve the complexity and workflow issues commonly associated with IGA.
IAM Hub: The platform acts as an “IAM Hub” that connects to existing systems to improve the flow and transformation of identity data.
Data Management: They offer inline data analysis and transformation capabilities, including a feature called “Atlas,” which serves as a meta-directory or virtual directory.
Solution Scenarios:
Addressing IGA Pain Points: They specifically target “IGA projects in distress” and enterprises that lack the ability to create complex connectors or workflows.
Productivity and Efficiency: Aiming to remove the human element in identity flows and serving as a productive driver.
Speed and Agility: Offering faster deployments and an adaptive platform that does not require changing existing processes.
StackBob
Core Capabilities:
Stackbob's primary focus is on IAM-infrastructure optimization and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA). Their solution implements alongside and augments existing IGA/IdP systems (like Sailpoint, MS Entra, and Ping), rather than replacing them.
Extending Governance to Any App: They specialize in bringing applications that lack standard connectors (SCIM or APIs) into the identity workflow, offering a “No API required” and “No-Code setup” approach.
Automating Identity Lifecycle: They help IT Admins and Department Managers streamline the joiner, mover, and leaver process (on/offboarding) and manage Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for employees and contractors.
Cutting License Waste: The platform helps Finance teams detect and remove unused licenses and orphaned accounts to reduce software costs.
Streamlining Security Compliance: They help businesses achieve audit-ready compliance evidence quickly for audits like SOC 2 and ISO 27001.
Agentic Approach: The company is moving to an “agentic and ultimately autonomous approach” to enhance workflows and manual fulfillment processes, as noted in your meeting files.
Solution Scenarios:
Automating Provisioning for Non-Integrated Apps (Joiner/Mover/Leaver)
Stackbob’s agentic technology can interact with the app’s user interface or other less-conventional interfaces to automate the provisioning and de-provisioning process.
Reducing Unused/Orphaned Software Licenses
The platform aggregates usage data and cost information across all managed apps to identify licenses that have low or no recent activity. It can then automate the process of either downgrading or deactivating these unused licenses, allowing teams to quickly realize savings and reduce license waste.
Achieving Audit-Ready Compliance for All Apps
Stackbob centralizes the access data for all applications, even those without APIs, providing a single source of truth for all users and their permissions. This makes it possible to quickly generate the comprehensive reports and evidence needed to pass audits, proving that Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) principles are applied
Pathlock
Core Capabilities:
Pathlock's core capabilities are centered around a comprehensive Identity and Application Access Governance (AAG) suite, specifically designed for fine-grained security and compliance in business-critical applications, particularly ERP systems. The solution is built on the vision of Continuous Access Governance for the Connected Enterprise.
Access Risk Analysis (ARA): Analyzes access risk for Segregation of Duties (SoD), Sensitive Access, and Critical Access in a single view.
Compliant Provisioning: Automates access provisioning with risk scoring and policy-based workflows.
Certifications: Facilitates the review of user access, roles, risks, and controls across all business applications.
Role Management: Helps build compliant technical and business roles with risk simulation analysis.
Elevated Access Management (EAM): Monitors privileged users, enforces controls, collects logs, and automates the review of high-risk activity.
Continuous Controls Monitoring: Provides real-time visibility into access, risk, and control events, moving from transaction-based to risk-based audit.
Cybersecurity Application Controls: Includes vulnerability management, threat detection and response, dynamic access controls, code scanning, and transport control.
Fine-Grained Entitlement Granularity: The platform provides a unique competency to perform fine-grained access risk management for multiple applications (e.g., SAP, Oracle EBS), going deeper than the coarse-grained entitlements of traditional IGA tools.
Solution Scenarios:
Replacing and Augmenting Legacy IGA and GRC Tools
Augment Existing IGA: Integrate with solutions like SailPoint and Microsoft Entra ID to provide the fine-grained Access Risk Analysis (ARA) for critical systems, enhancing their provisioning and certification workflows.
Replace Legacy Systems: Directly replace older systems by offering full Pathlock Cloud, more Out-of-the-Box (OOTB) rules, and superior multi-app capabilities (e.g., better Firefighter for emergency access).
Continuous Compliance and Audit Automation
Automate Controls Testing & Ensure Audit Readiness: Provide continuous, real-time evidence and centralized, standardized monitoring of all Segregation of Duties (SoD) risks across environments (SAP, JD Edwards, Ariba).
AI-Driven Audit: Future capabilities include “AI-generated documentation and audit evidence” and a “Chat with Your Auditor” explainable AI interface to streamline audit responses.
Fine-Grained Access Risk Management for Business-Critical ERPs
Visibility into Transaction-Level Activity: Captures granular, security-relevant user activity (page, field, transaction level) inside applications like PeopleSoft to see what a user is actually doing versus what they are provisioned to do.
Detailed Entitlement Granularity: For systems like Oracle EBS, Pathlock goes beyond simple roles to manage access across “App Specific Responsibilities,” “Functions Only with Prompt,” and “Consider ReadOnly Functions” to deliver precise risk reporting.
Non-Human Identity (NHI) Governance: Provides end-to-end governance for service accounts and agentic AI agents within ERPs, including request, provisioning, monitoring, and certification.
Zluri
Core Capabilities:
The Zluri platform is centered around its Next-Gen Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) approach, often described using the Visibility, Intelligence, Action (VIA) Model.
Visibility (SaaS Management & Discovery)
Comprehensive Application Visibility: Discovers and tracks all applications in use, including federated, unfederated, and Shadow IT apps.
Real-Time Usage Data: Moves beyond static identity attributes by integrating dynamic application activity data, crucial for optimization and risk analysis.
Gen AI Discovery: Identifies and auto-classifies Generative AI (GenAI) apps like ChatGPT and Claude in use across the organization.
Intelligence (Analytics & Reporting)
Zluri IRIS (Identity Risk Intelligence System): Provides interactive dashboards, pre-built widgets, and scheduled reports to track identity governance metrics, risk posture, and license utilization.
App Access & Activity Intelligence: Highlights insights such as unauthorized apps in use, over-provisioned access (e.g., users with admin access who don’t use it), and unused licenses.
License Optimization: Performs usage analysis to identify unused licenses and redundant applications, leading to significant cost savings.
Action (Automation & Governance)
Identity Lifecycle Management: Provides Instant Onboarding and Offboarding by bridging the HR-IT gap, using centralized playbooks to automate provisioning and deprovisioning actions across various systems (e.g., Okta, GitHub, Microsoft 365).
Access Reviews/Certifications: Simplifies audits (SOC 2, ISO 27001) with automated, evidence-based certification, where reviewer decisions are supported by actual usage data.
Entitlement Management & Least Privilege: Offers a centralized view of roles and permissions to support accurate review decisions and continuously rightsize permissions to reduce access sprawl.
Security & Compliance: Enables automated actions and alerts on policy violations and provides audit-ready reports.
Solution Scenarios:
Automated Onboarding and Offboarding (Identity Lifecycle Management)
Zluri automatically triggers a pre-configured workflow/playbook based on the HR system update (e.g., Workday or HiBob). It instantly provisions or deprovisions access across all required applications (like Okta, GitHub, Microsoft 365, Slack, etc.)
Evidence-Based Access Reviews and Compliance
Automates the process by initiating a certification campaign (e.g., “SOX ITGC Q2”). It provides reviewers with real-time usage and activity data for each user and entitlement. This “evidence-based certification” helps reviewers make accurate decisions.
SaaS Cost Optimization and Shadow IT Remediation
Patented Discovery Engine provides complete visibility into all 1400+ applications in use (Shadow IT included). It identifies “dormant” or “inactive licensed users” who are still paying for a license but haven’t used the app in a set time (e.g., 90 days).